Volume 23, Issue 4 (October & November 2020)
J Arak Uni Med Sci 2020, 23(4): 524-539 |
Back to browse issues page
Download citation:
BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:



BibTeX | RIS | EndNote | Medlars | ProCite | Reference Manager | RefWorks
Send citation to:
Heidari Soureshjani F, Kheirollahi M, Yaghmaei P, Sotoodehnejadnematalahi F. Effect of Donepezil and Hyoscyamoside on Improving Spatial Memory in Rats With Alzheimer's Disease. J Arak Uni Med Sci 2020; 23 (4) :524-539
URL: http://jams.arakmu.ac.ir/article-1-6263-en.html
URL: http://jams.arakmu.ac.ir/article-1-6263-en.html
Fatemeh Heidari Soureshjani1 

 , Majid Kheirollahi2
, Majid Kheirollahi2 

 , Parichehreh Yaghmaei1
, Parichehreh Yaghmaei1 

 , Fattah Sotoodehnejadnematalahi1
, Fattah Sotoodehnejadnematalahi1 




 , Majid Kheirollahi2
, Majid Kheirollahi2 

 , Parichehreh Yaghmaei1
, Parichehreh Yaghmaei1 

 , Fattah Sotoodehnejadnematalahi1
, Fattah Sotoodehnejadnematalahi1 


1- Department of Biology, Faculty of Basic Sciences, Science and Research Branch, Islamic Azad University, Tehran, Iran.
2- Department of Genetics and Molecular Biology, School of Medicine, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. ,mkheirollahi@med.mui.ac.ir
2- Department of Genetics and Molecular Biology, School of Medicine, Isfahan University of Medical Sciences, Isfahan, Iran. ,
Full-Text [PDF 7282 kb]
(1926 Downloads)
| Abstract (HTML) (3343 Views)
Full-Text: (3702 Views)
1. Introduction
lzheimer’s Disease (AD) is a neurodegenerative disease that is associated with profound impairments of memory and cognitive functions. In this disease, amyloid accumulation with hyperphosphorylation of tau protein, creating oxidative stress, inflammation, altered secretion of mediators, inhibition of synaptic plasticity, decreased number and function of cholinergic neurons, and eventually cell death. Research has shown that the use of steroid saponins reduces pro-inflammatory factors in the brain. Other benefits include their antioxidant and anti-acetylcholinesterase properties [5].
The use of medicinal plants with low side effects and antioxidant properties has received much attention. Therefore, we investigated the effect of sapogenin (hyoscyamoside) on spatial memory, and perhaps it can be used as a dietary supplement for families with hereditary Alzheimer’s disease in the prevention, delay of pathology, and treatment of this disease.
The use of medicinal plants with low side effects and antioxidant properties has received much attention. Therefore, we investigated the effect of sapogenin (hyoscyamoside) on spatial memory, and perhaps it can be used as a dietary supplement for families with hereditary Alzheimer’s disease in the prevention, delay of pathology, and treatment of this disease.
2. Materials and Methods
In the present experimental study, 60 male Wistar rats, approximately 7 weeks old, were divided into the following groups: control group, consisted of rats that received normal water and food; PBS group underwent surgery and received PBS (Aβ solvent); the first Alzheimer’s group consisted of rats that received beta amyloid during Alzheimer’s surgery; the second Alzheimer’s group received 1 cc of normal saline daily after Alzheimer’s surgery; the treatment groups, after beta-amyloid induction of Alzheimer’s disease in the rats, received 10 mg/kg of hyoscyamoside for 28 days in the hyoscyamoside group; the donepezil group received 4 mg/kg of this substance by gavage for 28 days.
Morris Water Maze (MWM) test was used to assess learning and memory. Due to the lack of differences in the initial results of the MWM test in the control group and PBS group, the control group was considered as the control group and therefore the second Alzheimer’s group was considered as the Alzheimer’s group. In this study, SPSS software V. 22 was used. To investigate the existence of significant differences between the groups, Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and post hoc tests were used according to the data.
Morris Water Maze (MWM) test was used to assess learning and memory. Due to the lack of differences in the initial results of the MWM test in the control group and PBS group, the control group was considered as the control group and therefore the second Alzheimer’s group was considered as the Alzheimer’s group. In this study, SPSS software V. 22 was used. To investigate the existence of significant differences between the groups, Analysis of Variance (ANOVA) and post hoc tests were used according to the data.
3. Results
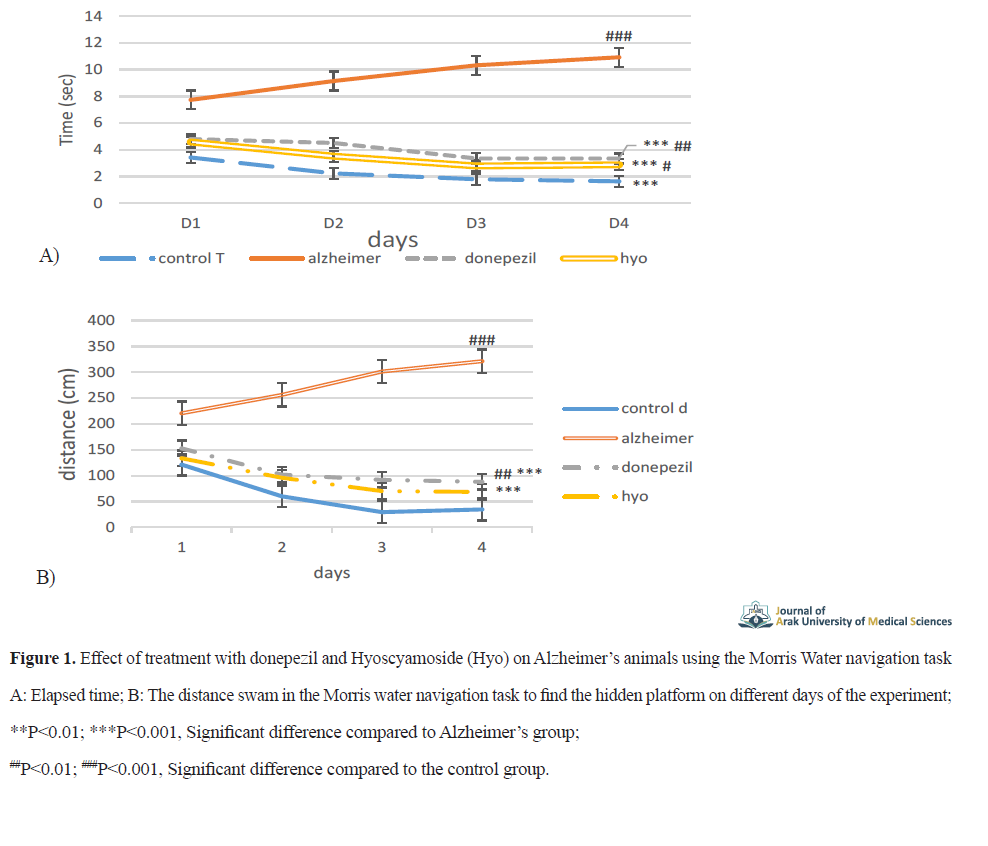
MWM test was used to evaluate spatial learning and memory. The results showed that the learning and spatial memory of the rats that received Aβ as an intra-hippocampal injection were impaired (P<0.001). The time elapsed and the distance traveled to reach the hidden platform, in the first to third days of training were considered as the criteria for learning, and on the fourth day after learning, they were considered as the criteria for verification. Alzheimer’s rats spent significantly more time and distance to find the hidden platform than the control group (P<0.001).
The treatment groups showed a significant decrease (P<0.001) compared to the Alzheimer’s group. On the fourth day, the hyoscyamoside group showed a significant difference (P<0.05) in the elapsed time compared to the control group. The donepezil treatment group showed a significant difference (P<0.05) compared to the hyoscyamoside group. Regarding the distance traveled, the donepezil group showed a significant difference (P<0.01) compared to the control group, while the hyoscyamoside group had a significant difference (P<0.01) compared to the control group. In the treatment groups, significant improvement in learning disability and spatial memory of Aβ-receiving rats were observed (P<0.001). The elapsed time and distance traveled to reach the hidden platform in the rats in the treatment groups decreased compared to the Alzheimer’s group (Figure 1).
In the dot-probe test, Figure 2 showed a significant increase in the time spent in the target quadrant by the treatment groups compared to the Alzheimer’s group (P<0.001), and this showed the positive effect of treatments on learning and spatial memory of Alzheimer’s rats. The treatment groups were not significantly different from each other and the control group (P<0.05).

The treatment groups showed a significant decrease (P<0.001) compared to the Alzheimer’s group. On the fourth day, the hyoscyamoside group showed a significant difference (P<0.05) in the elapsed time compared to the control group. The donepezil treatment group showed a significant difference (P<0.05) compared to the hyoscyamoside group. Regarding the distance traveled, the donepezil group showed a significant difference (P<0.01) compared to the control group, while the hyoscyamoside group had a significant difference (P<0.01) compared to the control group. In the treatment groups, significant improvement in learning disability and spatial memory of Aβ-receiving rats were observed (P<0.001). The elapsed time and distance traveled to reach the hidden platform in the rats in the treatment groups decreased compared to the Alzheimer’s group (Figure 1).

In the dot-probe test, Figure 2 showed a significant increase in the time spent in the target quadrant by the treatment groups compared to the Alzheimer’s group (P<0.001), and this showed the positive effect of treatments on learning and spatial memory of Alzheimer’s rats. The treatment groups were not significantly different from each other and the control group (P<0.05).

4. Discussion and Conclusion
In this study, Alzheimer’s disease in rats reduced their spatial memory, and their spatial memory improved after treatments. The time and the distance to reach the podium in the rats’ treatment groups were significantly reduced compared to the Alzheimer’s group (Figure 1). Studies showed that induction of Alzheimer’s disease in rats by Aβ1-42, reduced their memory, and triggered an inflammatory response. Treatment with donepezil improved Alzheimer’s rats’ performance on the Morris water navigation task and reduced their inflammatory cytokines [16].
The use of the steroidal saponin diosgenin in mutant rats improved their memory and showed that the diosgenin treatment group removed Aβ plaque, reduced neuronal death and neurofibrillary tangles in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus, and inhibited acetylcholinesterase [15]. Sapogenins with antioxidant properties inhibit IL-6 and TNFα and inhibit their production of free radicals [27].
Researchers are trying to develop drugs that, in addition to having better effects, also have fewer side effects. Plants are one of the sources that have always been used for the production of new medicines [17]. The present results showed that the use of donepezil and hyoscyamoside improved memory. The treatments may have improved the condition of plaque formation and memory loss (due to plaque) and cholinergic system defects, which may be due to the inhibitory activity of acetylcholinesterase and antioxidants.
The use of the steroidal saponin diosgenin in mutant rats improved their memory and showed that the diosgenin treatment group removed Aβ plaque, reduced neuronal death and neurofibrillary tangles in the cerebral cortex and hippocampus, and inhibited acetylcholinesterase [15]. Sapogenins with antioxidant properties inhibit IL-6 and TNFα and inhibit their production of free radicals [27].
Researchers are trying to develop drugs that, in addition to having better effects, also have fewer side effects. Plants are one of the sources that have always been used for the production of new medicines [17]. The present results showed that the use of donepezil and hyoscyamoside improved memory. The treatments may have improved the condition of plaque formation and memory loss (due to plaque) and cholinergic system defects, which may be due to the inhibitory activity of acetylcholinesterase and antioxidants.
5. Conclusion
According to the results of studies in people at high risk of Alzheimer’s disease, it is suggested that the use of hyoscyamoside and donepezil be included in their daily diet for prevention. In people with Alzheimer’s, taking hyoscyamoside may improve the disease, possibly by influencing the causes of Alzheimer’s (such as accumulated beta-amyloid plaque, cholinergic system disorders, oxidative stress, and inflammation), and prevention of neuronal apoptosis improves the disease and prevents familial cases of Alzheimer’s.
Ethical Considerations
Compliance with ethical guidelines
This research was ethically approved by the Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch (Code: REC.1397.057. IR.IAU.SRB).
This research was ethically approved by the Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch (Code: REC.1397.057. IR.IAU.SRB).
Funding
The paper was extracted from the PhD. dissertation of the first author, Department of Biology, Islamic Azad University, Science and Research Branch, Tehran.
Authors' contributions
All authors met the standard writing criteria based on the recommendations of the International Committee of Medical Journal Publishers (ICMJE) and all contributed equally to the writing of the work.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declared no conflict of interest.
Acknowledgements
This article was taken from a doctoral dissertation and has no sponsorship. We are grateful to all those who cooperated with us in conducting this research.
Type of Study: Original Atricle |
Subject:
Basic Sciences
Received: 2020/03/16 | Accepted: 2020/08/26
Received: 2020/03/16 | Accepted: 2020/08/26
Send email to the article author
| Rights and permissions | |
 |
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License. |






